Use Case Prioritization Framework for AI Products

Companies turning to artificial intelligence (AI) for business solutions face a tough decision: Which use cases will bring the most business value? AI adoption is often expensive and complicated, placing organizational leaders at odds with one another on which use cases to prioritize. According to Gartner, 73% of CIOs say their organizations are increasing AI investment in 2024, while 67% of CFOs report that AI initiatives have underperformed expectations, revealing a dangerous fault line in the AI landscape.
To help AI product managers and company stakeholders reach a consensus on AI solutions that meet or exceed expectations, I’ve developed a new use case prioritization framework called the Gen AI Strategic Alignment and Impact Framework (GSAIF). As the name suggests, I designed the framework for generative AI (Gen AI) use cases in particular. Common frameworks (e.g., the impact-effort matrix or the cost of delay model) are typically rooted in financial metrics and struggle to capture the unique characteristics of Gen AI, such as the potential for exponential growth, the rapid pace of technological change, and novel ethical considerations.
GSAIF involves a two-phase prioritization process that begins with a qualitative screening followed by a detailed multicriteria evaluation using a weighted scoring model. To illustrate how the framework functions, I present a real-world case study alongside a step-by-step explanation of the method I developed. The case study focuses on a small e-commerce business that was searching for AI solutions to challenges that impeded the company’s growth and ability to engage and retain customers effectively.
This article provides a detailed walkthrough of the impediments the business faced, the potential AI solutions identified by stakeholders, and the GSAIF review that enabled us to evaluate and prioritize solutions. As the case study shows, the solution we selected for product development yielded a huge impact for the company, increasing its customer retention rate by a factor of three. I encourage product managers and other business leaders who are facing the same AI adoption challenges to use the GSAIF template available at the end of the article.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
The e-commerce company at the center of this case study is based in the United States and offers more than 5,000 products across multiple categories, including apparel, electronics, home goods, and beauty products. At the outset of its AI adoption process, the company identified five key areas requiring improvements to enhance the customer experience, streamline operations, and, ultimately, boost profitability.
The challenges included:
- Lack of a personalized customer experience: The business struggled to provide a personalized shopping experience, leading to a customer retention rate of only 20%, significantly below the industry average of nearly 30% for e-commerce brands.
- Inefficient customer service: The business’s customer service model was not equipped to handle queries efficiently, resulting in an average wait time of 10 minutes for customer support via channels like chat or phone, leading to a customer dissatisfaction rate of 40%.
- Suboptimal product descriptions: Based on an SEO analysis, staff identified that product descriptions on the e-commerce platform were too generic and failed to engage potential buyers. Only 25% of product pages had descriptions that effectively matched search queries.
- Inadequate inventory management: The company faced challenges in accurately predicting stock levels, leading to overstock situations for 30% of its inventory and stockouts for 20% of its most popular items.
- Overly broad marketing efforts: Marketing strategies were not sufficiently targeted, leading to a lower ROI on marketing spend with a return of just $2 for every $1 spent, compared to a common industry benchmark of $4.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Generative AI Solutions
To address the business challenges the company had identified, I was brought in as a strategic product consultant to lead a three-hour brainstorming workshop with business stakeholders. During this collaborative session, we explored the potential of generative AI to transform the company’s operations, taking into consideration its existing technology infrastructure and data availability.
We identified the following potential product initiatives as relevant to each business challenge:
- Personalized recommendation system: A system that leverages AI for customer data and generates personalized product recommendations on the webpage could enhance the user experience and increase sales.
- Chatbots for enhanced customer service: AI-powered chatbots could provide instant, 24/7 customer support and personalized shopping assistance, thereby improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- Content generation for product descriptions: Generative AI tools could be used to create unique, engaging, and SEO-friendly product descriptions, which could help improve product visibility and conversion rates.
- Inventory management: AI algorithms could be implemented to accurately forecast demand and optimize inventory levels, reducing the incidence of overstock and stockouts and improving supply chain efficiency.
- Personalized email marketing campaigns: AI could be used to analyze customer behavior and craft highly targeted marketing strategies through email drip campaigns, thereby increasing the effectiveness of marketing efforts and enhancing customer engagement.
Other ideas emerged during the brainstorming session, but we selected these five Gen AI use cases for further evaluation based on their potential to directly address the identified business challenges.
Step 3: Conduct the Initial GSAIF Screening Phase
Now that we had identified five promising Gen AI use cases for the e-commerce company, a new challenge arose: We needed to determine which of these product options to prioritize. This is a common dilemma when resources are limited—and the wrong choice can be costly.
The initial screening stage of the framework’s two-phased approach was conducted during a portion of the focused workshop in which we assessed the use cases qualitatively, evaluating the following factors on a scale of low, moderate, or high:
- Feasibility: What is the ease of implementation given our current technology and resources? Are there any major roadblocks or limitations, including compliance with regulations and ethical considerations?
- Cost: What is the estimated cost of developing and implementing this solution? Does it fit within budget constraints?
- Impact: How much potential does this use case have to impact the business positively? Will it move the needle on key metrics?
- Alignment with business goals: Does this use case directly address strategic objectives? Does it align with overall vision and mission?
When screening use cases at this stage of the strategic prioritization framework, the importance of each factor can vary depending on the specific context and the organization’s strategic goals. For instance, the balance between cost versus impact may differ from business to business. Is it better to have a moderate-cost, moderate-impact solution? Or would it be better to focus on one that is high cost but high impact? There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, as the ideal balance depends on several factors, including:
- Budget constraints: Organizations with limited budgets may prioritize lower-cost solutions with moderate impact, aiming for quick wins and tangible results.
- Risk tolerance: If an organization is comfortable with higher risk, it may invest in high-cost, high-impact projects with the potential for significant returns.
- Strategic goals: The alignment of a use case with overarching strategic goals can sometimes outweigh cost considerations, especially if the potential impact is transformative.
- Time horizon: Meeting short-term financial goals might privilege lower-cost projects, while implementing long-term growth strategies might justify higher up-front investments for potentially greater long-term impact.
To account for these considerations, I collaborated with stakeholders at the e-commerce company to determine the relative importance of each factor in the decision-making process. This screening ensured that we focused resources on product development opportunities with the highest potential for success and alignment with the business’s long-term goals. Based on this comprehensive evaluation, we jointly identified three of the five use cases for additional evaluation:
- Selected use case 1: Personalized recommendation system
- Selected use case 2: Chatbots for enhanced customer service
- Selected use case 3: Content generation for product descriptions
We also screened out two use cases that were not strategically aligned, ethically sound, technically feasible, or compliant with relevant regulations:
- Nonselected use case 1: Inventory management
- Nonselected use case 2: Personalized email marketing campaigns
In the sections below, I explain the GSAIF screening results for each of these five use cases.
Selected Use Case 1: Personalized Recommendation System
We selected this use case due to its high potential to directly impact customer engagement and retention, aligning with the strategic goal of enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. By leveraging customer data to generate personalized product recommendations, the system addressed the challenge of providing a personalized shopping experience, which is crucial for a small e-commerce business looking to differentiate itself in a competitive market.
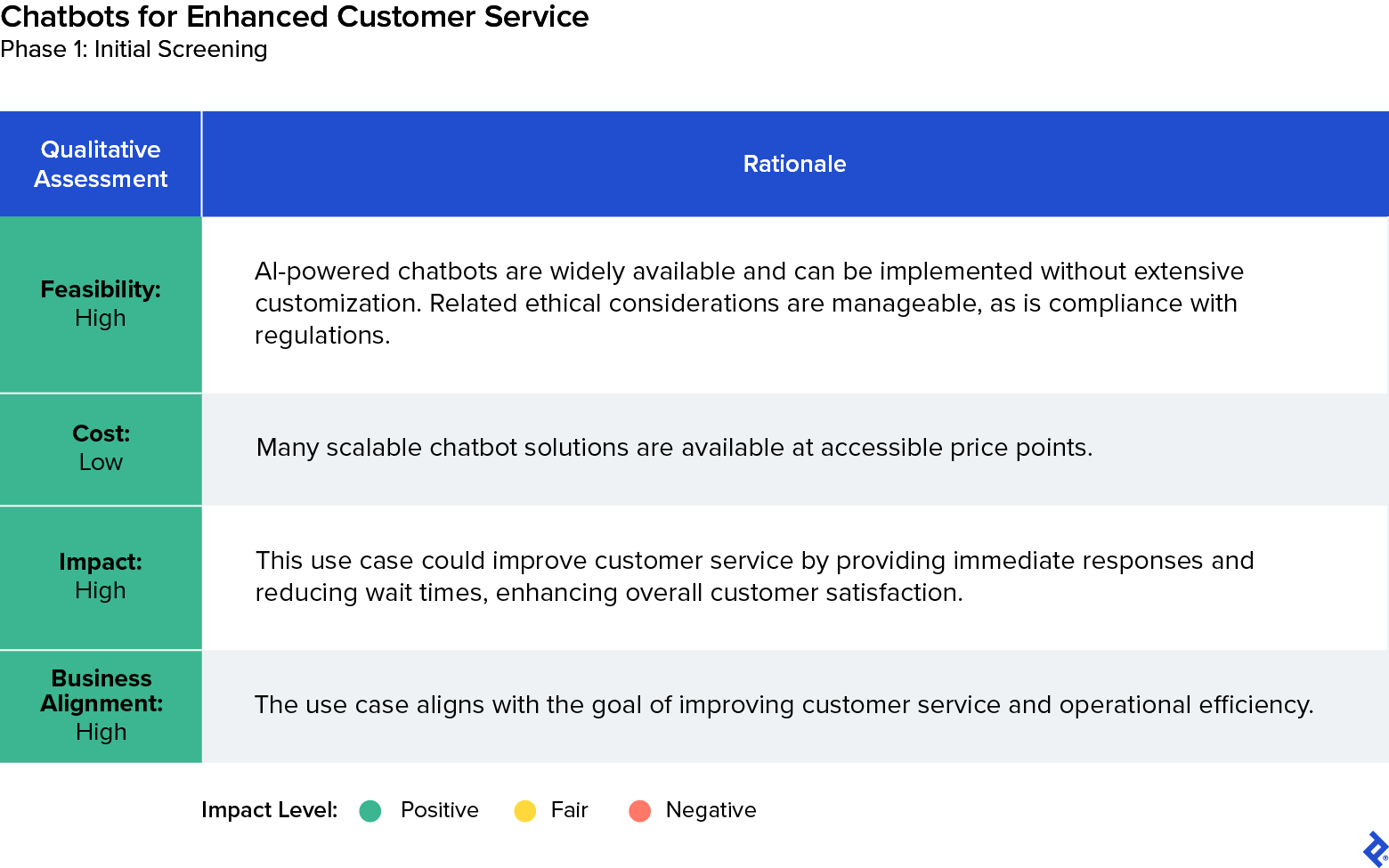
Selected Use Case 2: Chatbots for Enhanced Customer Service
We also determined that customer service chatbots warranted additional evaluation. This prioritization was grounded in the solution’s high feasibility, low cost, and significant impact on customer satisfaction. Chatbots could provide instant, 24/7 customer support and personalized shopping assistance, directly addressing the inefficiency of the current customer service model. We also appreciated that chatbots offered customization options that would allow the company to adhere to regulations and address ethical considerations, such as transparency about AI usage. Also, a customer service representative could provide fallback support, in the event that customers encountered issues with the chatbot experience. This solution promised relatively high ease of implementation and immediate benefits in operational efficiency.
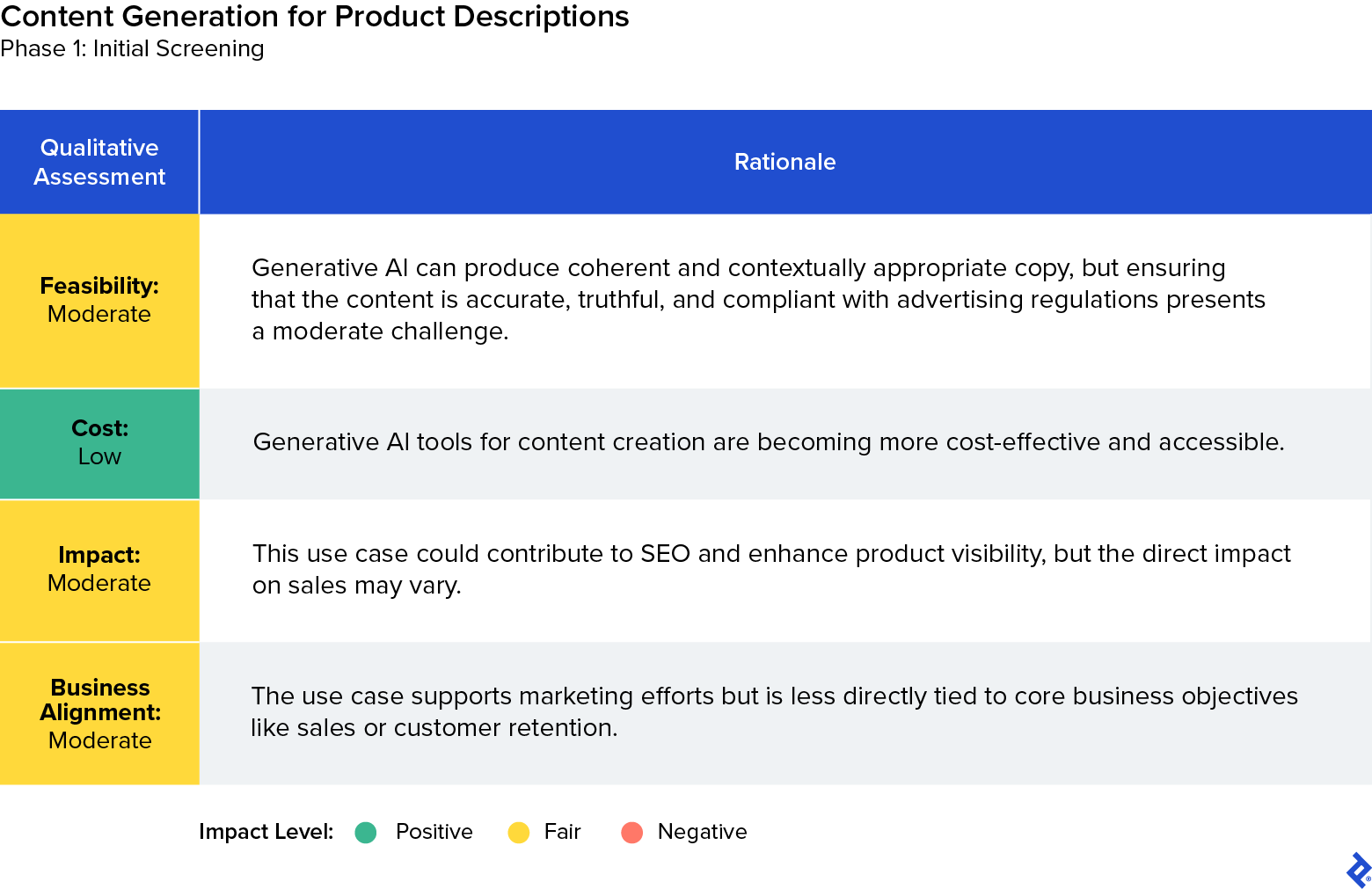
Selected Use Case 3: Content Generation for Product Descriptions
Based on the GSAIF screening criteria, we selected automated content generation for product descriptions as the third use case for additional evaluation. We recognized its potential to enhance product listings with unique, SEO-friendly descriptions at a low cost, directly addressing the challenge of suboptimal product descriptions. This use case aims to improve conversion rates by providing compelling product information while aligning with the GSAIF’s emphasis on innovation and competitive advantage. Moreover, the use case appeared to be reasonably feasible, further supporting its selection.
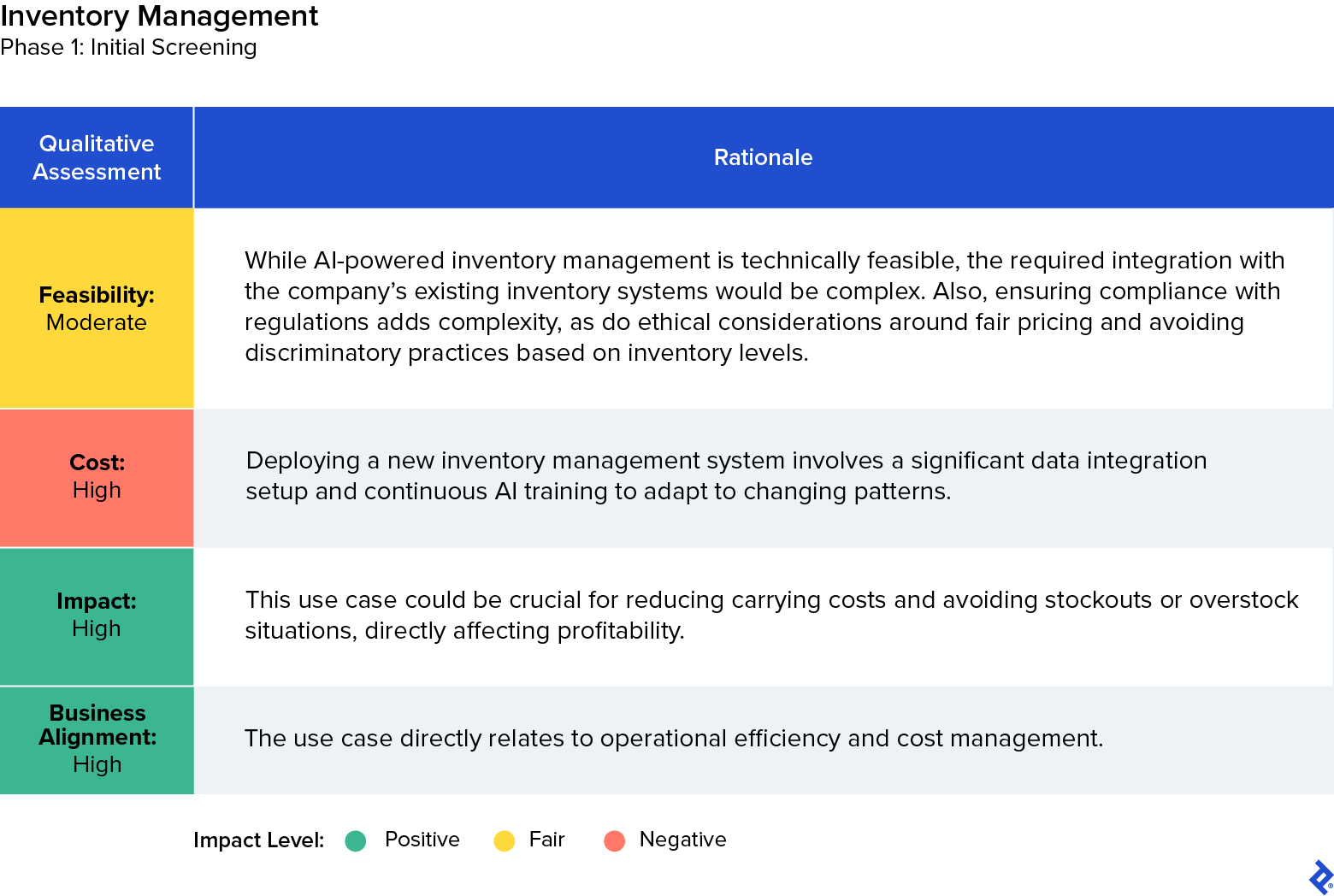
Nonselected Use Case 1: Inventory Management
We determined that AI-enabled inventory management did not warrant additional evaluation, despite its potential to improve supply chain efficiency by accurately predicting stock levels. For a small business, the significant investment required for implementation and the challenges associated with integrating advanced AI algorithms into existing inventory systems outweighed the immediate benefits, as did the need for compliance with data regulations and ethical inventory practices.
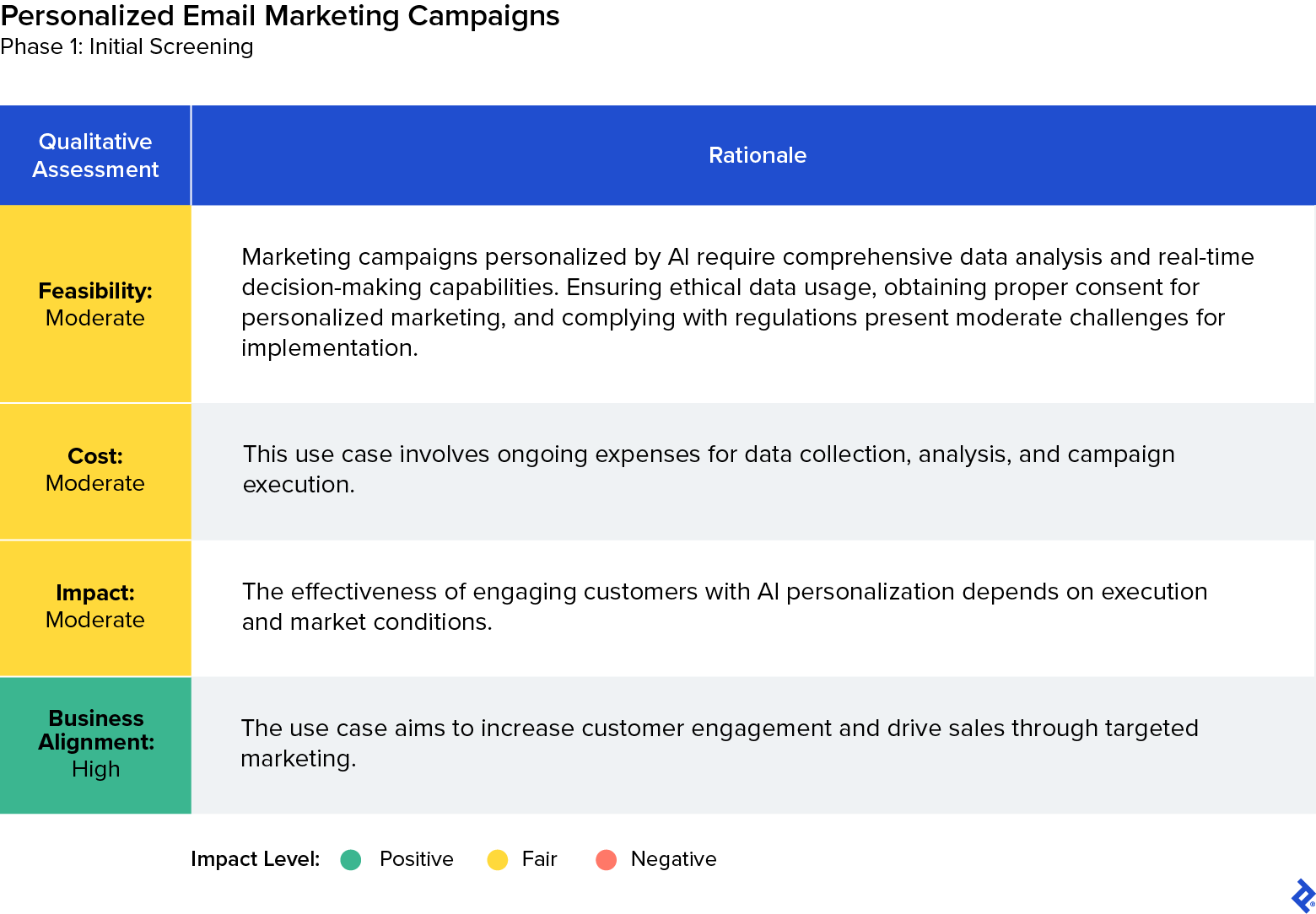
Nonselected Use Case 2: Personalized Email Marketing Campaigns
Although personalized marketing campaigns are valuable for targeting specific customer segments and improving marketing ROI, we determined that this use case would be less directly impactful compared to other options, such as automated content generation for product descriptions. A multifaceted analysis further solidified this decision. While both use cases held promise, automated content generation offered a more immediate and direct solution to the pressing issue of suboptimal product descriptions, aligning closely with the company’s in-the-moment needs and resource constraints.
Step 4: Conduct the GSAIF Detailed Evaluation Phase
Following the initial three-hour workshop, in which we identified three use cases that promised to have the biggest impact on the e-commerce company’s needs, my e-commerce client and I began the second phase of GSAIF. This phase involves in-depth research, data collection, and asynchronous input from stakeholders to populate a multicriteria scoring matrix that considers factors like scalability, innovation potential, and market viability.
The detailed evaluation allows for a comprehensive assessment of each AI use case to ensure that the ultimate prioritization would align with the organization’s objectives and deliver tangible, ethical, and compliant value.
This prioritization matrix used a scaled scoring system (1 to 10) based on the impact level for eight essential criteria:
- User demand and value proposition: What is the market demand for the proposed Gen AI solution, and what value does it offer to the user base? Does it align with customer needs and preferences?
- Cost and ROI analysis: What are the financial implications of implementing the Gen AI solution? What are the development, deployment, and maintenance costs? What is the potential return on investment through increased efficiency, revenue, or other benefits?
- Data availability and quality: What is the accessibility and quality of the data required to train and operate the Gen AI model? Are there potential challenges in obtaining or maintaining high-quality data?
- Scalability and integration: How easily can the solution be integrated into existing systems, and how well can it scale as the business grows?
- Competitive advantage: Does the use case offer a unique value proposition or competitive edge in the market?
- Operational impact and efficiency: How significantly will this solution improve operational efficiency and streamline processes?
- Risk assessment: What are the potential risks associated with this use case, and how can they be mitigated?
- Market trends and customer insights: Does the use case align with current market trends and address customer needs and preferences?
Each factor was then weighted according to its strategic significance for the specific scenario. The weights assigned to each are not fixed and can vary depending on the nature of the business and its specific strategic goals. For instance, a consumer-facing business might assign more weight to user demand and value proposition, given customer feedback or user experience insights. Meanwhile, a B2B organization might consider operational impact and efficiency to be more important.
In this case, we selected the following weights:
- User demand and value proposition and competitive advantage were each weighted at 15%, reflecting the importance of choosing a solution that resonated with customers and differentiated the business in the market.
- Cost and ROI analysis and operational impact and efficiency were also weighted at 15% each, emphasizing the need for a financially viable solution that could improve the company’s operations.
- The four remaining criteria—data availability and quality, scalability and integration, risk assessment, and market trends and customer insights—were each weighted at 10%, acknowledging their importance but giving them less priority compared to the factors mentioned above.
Thus, if we assigned a score of 10 for user demand and value proposition, it would contribute more to the overall score than a 10 assigned for risk assessment.
The determination of these weights was a collaborative process, involving discussions with stakeholders to ensure alignment with their priorities and the overall business strategy. It’s important to note that while the weighted scoring model provided a quantitative framework, the assignment of scores and weights involved both quantitative data analysis and qualitative judgment calls, informed by stakeholder input and independent research.
The outcome of the second phase of the GSAIF review is a rigorously quantified score for each use case. This single score enables product managers and other decision-makers to prioritize an AI solution with the highest strategic value and market relevance, ensuring the final decision is well-informed and aligned with the business’s long-term goals. In this case, the evaluation process allowed us to rank the three use cases selected during the screening phase in the following order:
- Highest evaluation score: Personalized recommendation system
- Intermediate evaluation score: Chatbots for enhanced customer service
- Lowest evaluation score: Content generation for product descriptions
In the following sections, I walk through the evaluation results for these three potential approaches.
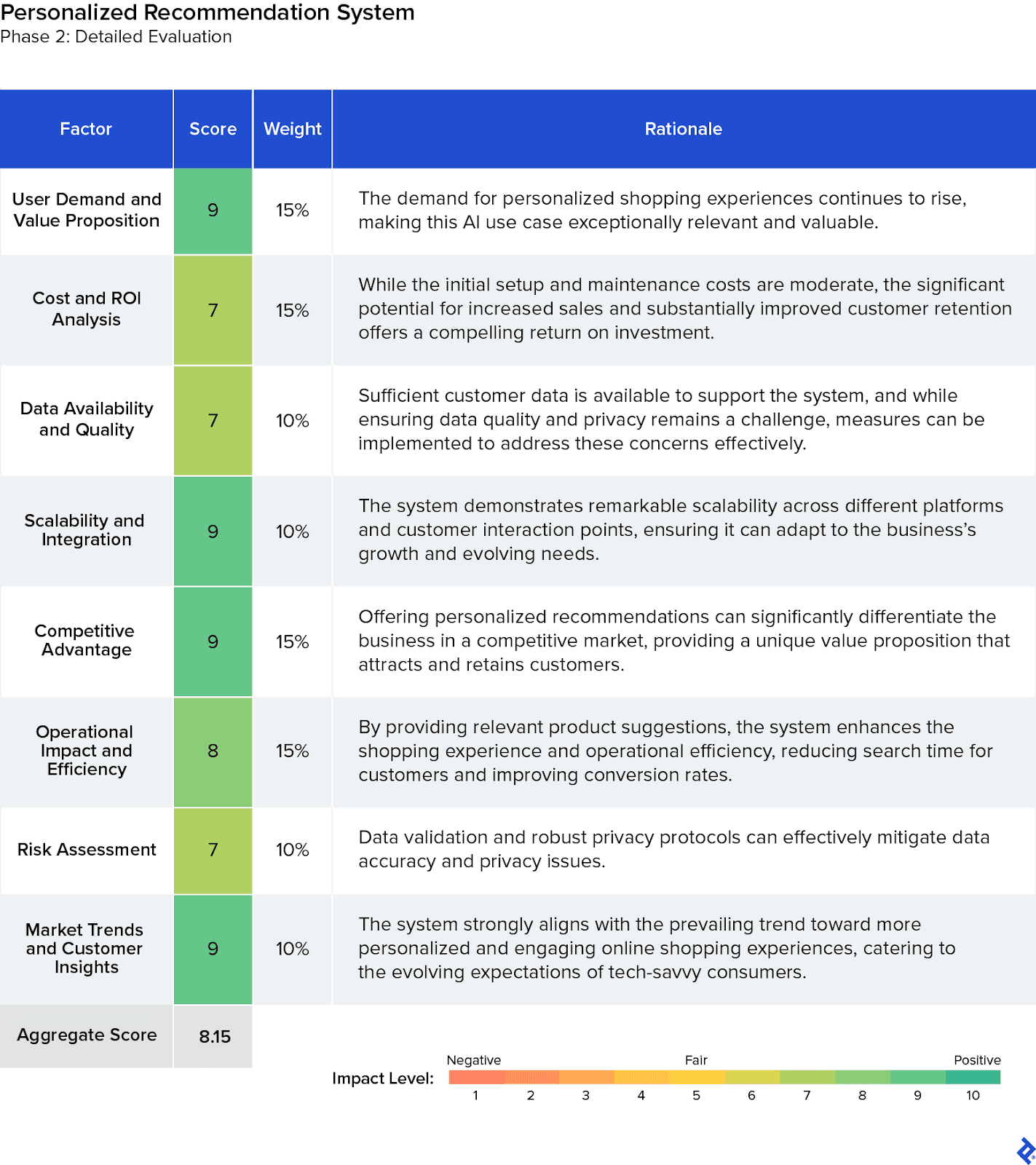
Highest Evaluation Score: Personalized Recommendation System
The AI-driven personalized recommendation system earned an aggregate evaluation score of 8.15, reflecting its strong alignment with market demands for tailored shopping experiences. This system also offered significant competitive advantages by differentiating the business in a crowded market; we also determined that the potential for increased sales and improved customer retention would justify the moderate initial costs. However, challenges such as maintaining data quality and privacy and the need for continuous system updates would present ongoing considerations for the product strategy.
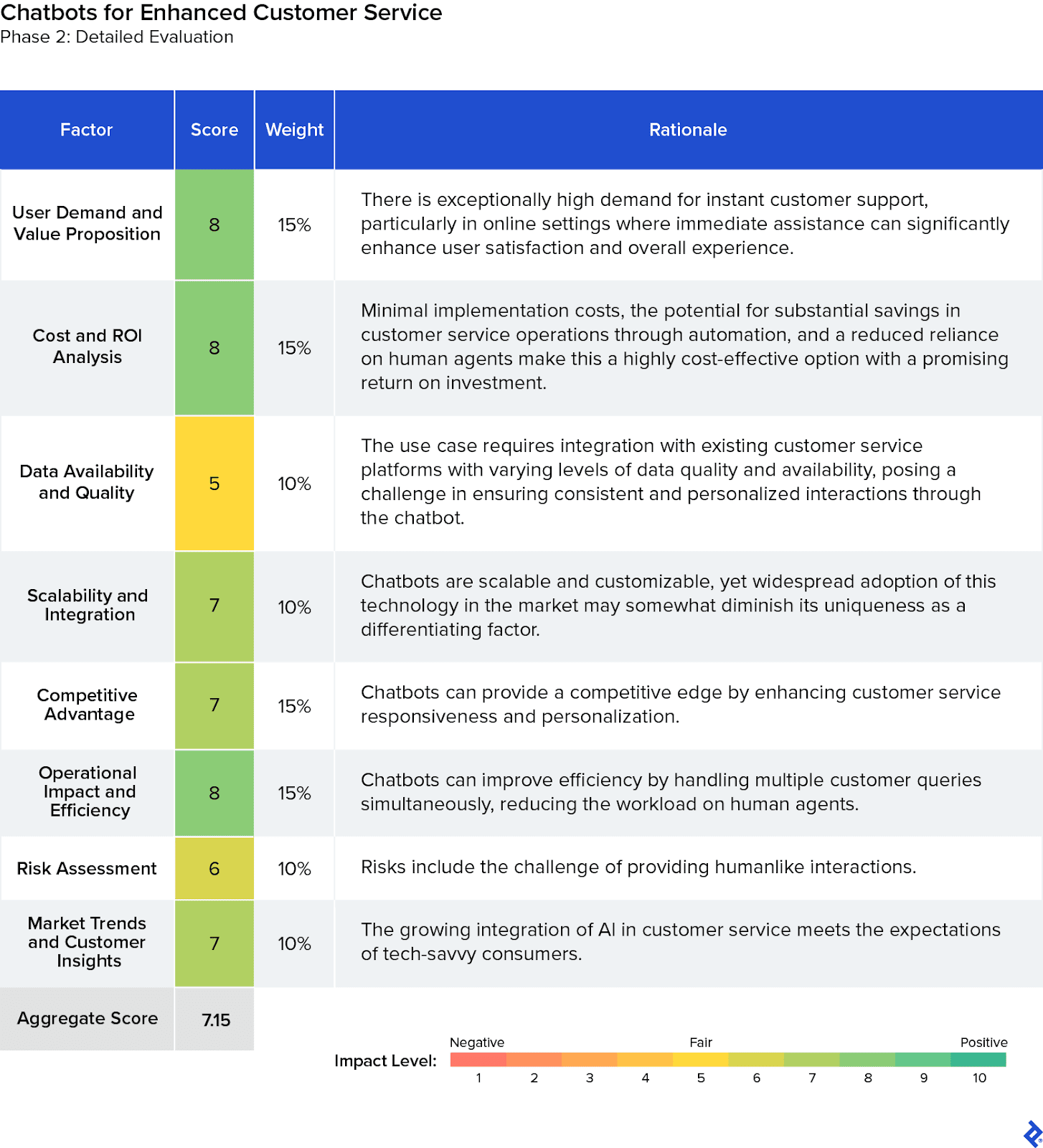
Intermediate Evaluation Score: Chatbots for Enhanced Customer Service
With an aggregate score of 7.15, this use case came in second, highlighting the importance of modernizing customer interactions. We recognized that AI chatbots would allow the company to respond to the high demand for instant support in digital environments, enhancing user satisfaction through rapid query resolution. Ease of implementation and scalability across various platforms makes chatbots a cost-effective solution for improving service efficiency. However, the variability in data quality and the potential for technical failures would require careful management to maintain service reliability and personalization.
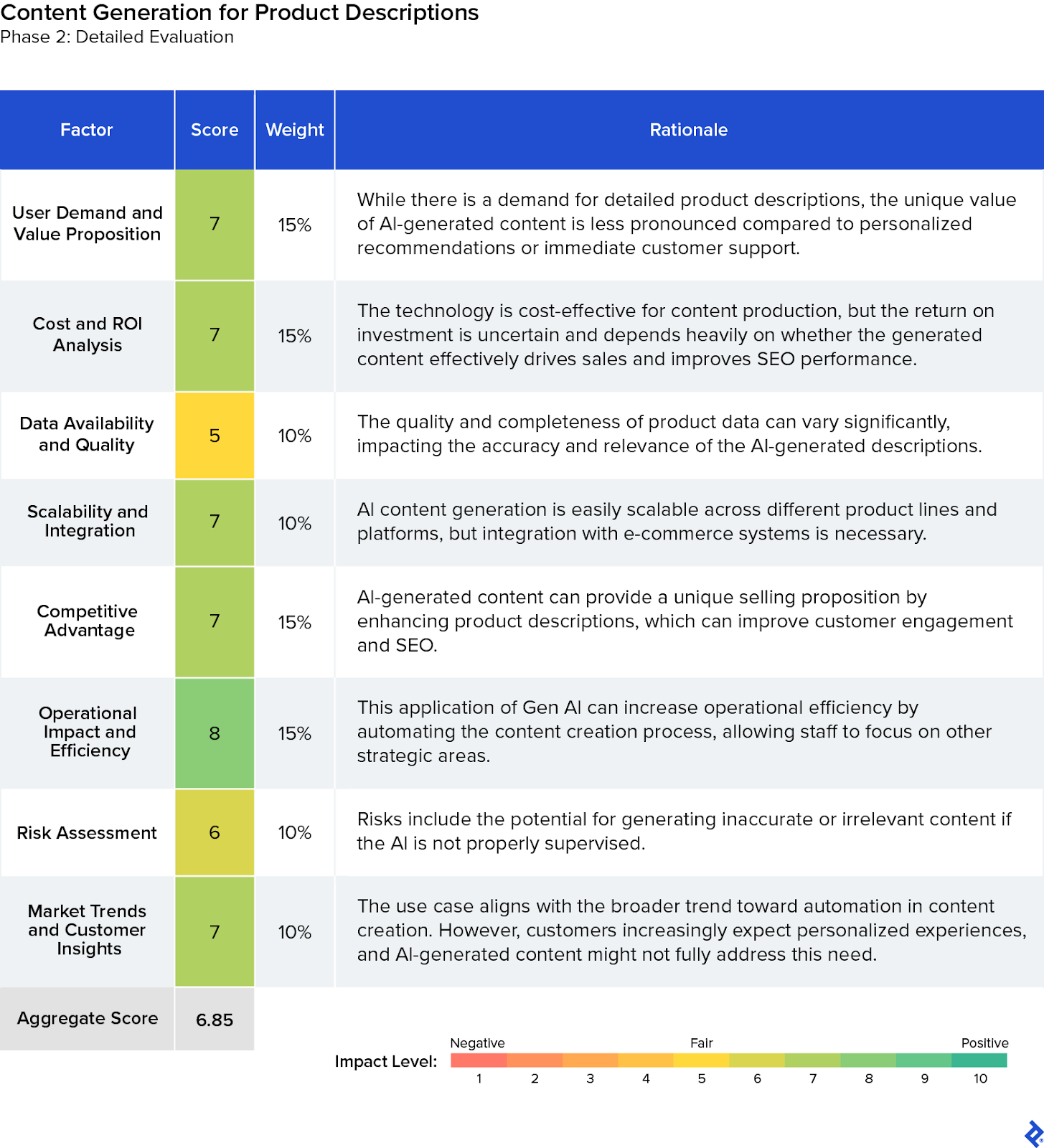
Lowest Evaluation Score: Content Generation for Product Descriptions
We determined that using AI content generation for product descriptions could capitalize on the high demand for engaging and detailed online content crucial for attracting and retaining e-commerce customers. Yet the aggregate score of 6.85 for this use case was the lowest rating among our three contenders. While an automated content generation system would offer significant operational efficiencies by automating content creation, the return on investment would depend heavily on the content’s impact on sales and SEO. We recognized that the company could face challenges ensuring the accuracy and relevance of the generated content, given that the process would necessitate ongoing supervision and integration with existing e-commerce systems.
Step 5: Implement and Evaluate Results
Based on the detailed evaluation using GSAIF, the e-commerce company elected to pursue an AI-driven personalized recommendation system, given it had emerged as the most suitable choice for addressing the business’s challenges with customer engagement and retention. This prioritization was not solely based on its aggregate score of 8.15—the highest of the three finalists—but also on the comprehensive analysis and collaborative discussions facilitated by the GSAIF evaluation process.
Armed with a clear understanding of the problem and a well-defined product vision, the company’s development team embarked on a proof-of-concept implementation of the AI-driven personalized recommendation system. The results were remarkable, with the customer retention rate increasing from 20% to a whopping 60%—double the industry average. This dramatic improvement underscores the effectiveness of GSAIF in identifying high-impact solutions that align with both business goals and customer needs.
A different outcome would likely have occurred if the company had relied on traditional prioritization frameworks. Common methods often focus on short-term financial metrics and might have led to a different choice, such as prioritizing chatbots for their immediate cost savings, perceived efficiency gains, and ease of implementation. However, the comprehensive and multifaceted approach of GSAIF enabled the company to recognize the transformative potential of personalized recommendations in driving customer loyalty and growth over a longer time frame.
GSAIF Template: Try This Strategic Prioritization Framework
The success of this real-world example showcases the power of GSAIF as more than just a use case prioritization framework. The GSAIF process fosters a shared understanding of the problems and potential of AI among diverse stakeholders. This alignment, coupled with the clarity provided by the detailed evaluation process, empowers companies and product managers to confidently navigate the complexities of AI adoption and invest in solutions that yield tangible and meaningful outcomes.
To activate these insights and leverage GSAIF’s full potential in your organization, I invite you to download the comprehensive GSAIF template. Use the template to begin your journey toward strategically aligning and prioritizing your Gen AI initiatives.



