Google Banner Ads: The Ultimate Guide For 2024

Whether you’re a startup ready to start using Google Ads or a small business that has been running some online ads by yourself or through a Google Ads freelancer, you likely have a very limited advertising budget. However, you still need your target audiences to know you exist.
The thing is, people aren’t going to search for you if they don’t know you exist. Although one of the best ways to capture user intent is still the Google Search Network (GSN), if people don’t know about your brand, products, or services, they simply won’t search for you.
This is where the Google Display Ads Network (GDN) comes in. Banner ads are the most common display ads, so the terms “banner ads” and “display ads” are often used interchangeably.
Google Banner Ads are image-based ads that show passively on the 35 million apps and websites on GDN, which includes all Google-owned properties, such as Gmail, Waze, and YouTube.
In 2022 alone, businesses worldwide spent $400 billion on online advertising. Google Ads, formerly Google AdWords, is one popular option for small to medium business owners who want their business to be seen by more of the 5.18 billion of internet users today. Google has 28% market share in the online advertising industry today, followed by Facebook at 25% share, then Alibaba at 9% share.
Google Ads, as Google AdWords then, started in 2000, two years after the Google Search engine was launched to promote products and services in Google search engine results pages (SERPs). Over time, Google Ads, particularly display or banner ads, were also shown on Google’s parent company site, as well as its owned companies’ apps and sites.
Google Display or Banner Ads reach 90% of all internet users worldwide, with more than a trillion impressions served to 1 billion users every month.
This guide helps you better understand what Google Banner Ads are, how they can best help your business, how to set up your banner ads, and what the best practices are in display or banner advertising.
What Are Google Banner Ads?
Google Banner Ads are image ads on apps or websites. They are rectangular ads that occupy a part of an app’s or website’s layout. While users interact with the app or website, banner ads remain onscreen.
Google Banner Ads are effective as they don’t take up too much space, they work well with many apps and websites, and they are the simplest display ad format to use. Google Banner Ads refresh automatically after a set time period.
You can link your banner ad to any URL or web address on your website, although most businesses prefer to link them to a specific landing page based on their marketing goal for that ad. Google Banner Ads usually contain minimal text, a focal image, and a clear Call-To-Action (CTA).
Google Banner Ads and Google Ads Campaign Types
Google Banner Ads are used for Display campaigns. Display campaigns are one campaign type available in Google Ads. Display campaigns serve visually engaging ads on the Google Display Network (GDN) which helps businesses reach millions of people as they browse apps, websites, and Google-owned properties.
The other types of Google Ads campaigns and what each campaign is about are:
- Performance max campaigns: to access all channels from a single campaign with automated optimization
- Search campaigns: for showing text ads on search results
- Video campaigns: for showing video ads on YouTube
- App campaigns: for promoting an app on many channels
- Local campaigns: for promoting a location on many channels
- Smart campaigns: for automated campaigns
- Shopping campaigns or Performance Max with Merchant Center feed: for product listings on Google
Google Ads begin with a marketing goal and a campaign. Based on your marketing goals, brand strategy, and budget, you then choose the appropriate campaign type.
Types of Google Banner Ads
There are now only two main types of Google Display Campaign Banner Ads: the Standard and Adaptive Banners.
There used to be three, with Smart Banners, but Smart Banners has been deprecated. “Deprecated” means that although something is available or allowed, it is not recommended because of its recognized weaknesses. This further means that it will soon be turned off. Adaptive Banners were intended to replace Smart Banners.
1. Standard Banners
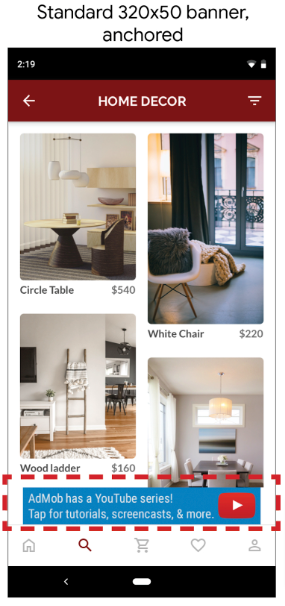
These fit only the specified banner size, or the container of your ad. The industry-standard banner size is 320×50 pixel density (dp).
If the container has white space or padding, this decreases the effective size of the container. If the container cannot fit the banner ad, the banner will not appear, and you get a warning in your logs saying that there is not enough space to show the ad. You will also get advice from Google on what size is needed.
2. Adaptive Banners
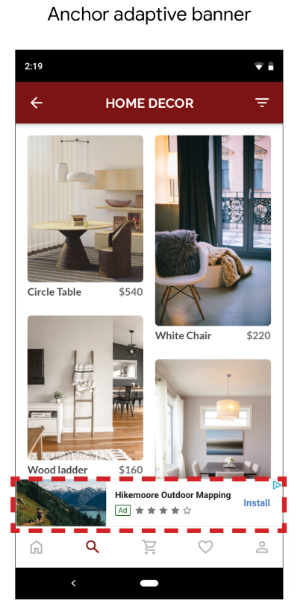
Adaptive banners are next-generation responsive ads. Responsive ads automatically adjust their appearance, format, and size to fit the available ad spaces.
For any given device or width, adaptive banners always return a constant size. However, the banner creative size may change across different devices. For example, an adaptive banner ad may appear as a simple text-based banner ad in one place and a large image banner ad in another place.
For the best ad size, adaptive banners use fixed aspect ratios rather than fixed heights. The adaptive banner ads then cover a more consistent portion of the screen across different devices, giving opportunities for improved performance.
There are two types of adaptive banners: anchored and inline. Anchored adaptive banners are always onscreen, locked at the top or bottom of the screen. Anchored adaptive banners usually have small maximum heights to avoid taking up too much space on the screen. Inline adaptive banners are placed inside scrollable content. Inline adaptive banners don’t have fixed size limits.
Adaptive banners are often used as anchored banners. The aspect ratio is similar to that of the standard 320×50 dp ad.
Adaptive banners aim to fill the entire ad slot size chosen, so Google selects creatives for best performance. This means that some ad creatives might fit an adaptive banner edge to edge, and some might be centered on the ad slot. This depends on which advertiser bids the highest for that ad slot’s impressions.
Adaptive banners can be used to replace any Standard Banner placements.
Google Banner Ads Sizes
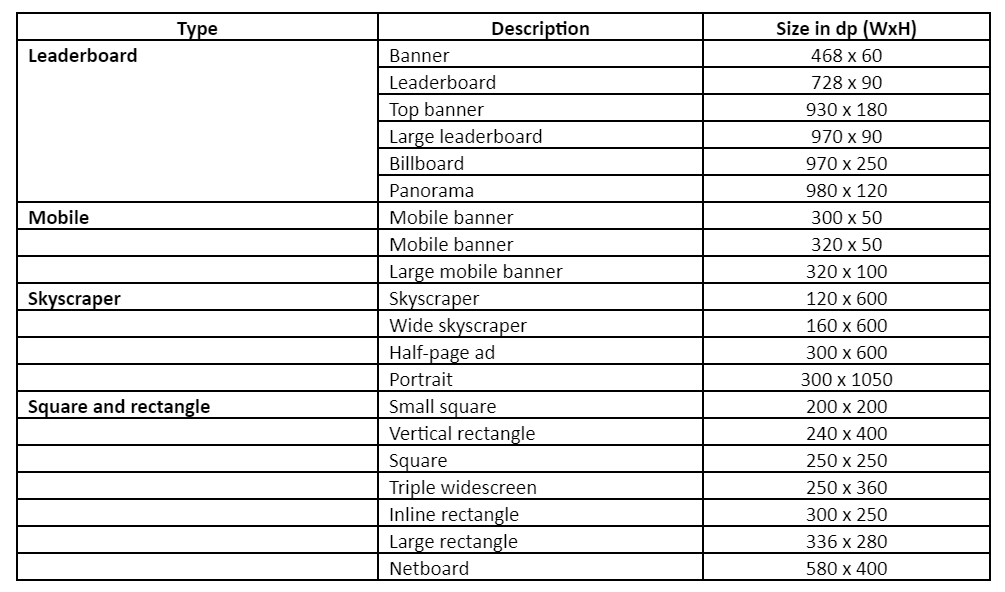
Banner ads may be static images or responsive ads. They should come in any of only three formats– GIF, JPG, or PNG – with a maximum size of 150 KB.
There are 20 non-animated banner ad sizes:
Animated banner ads in GIF format should have an animation length of not more than 30 seconds. They can be looped but must stop after 30 seconds. Animation ads should also be slower than five frames per second (FPS).
Google’s top-performing ad sizes are the:
- Medium rectangle (300 x 250)
- Large rectangle (336 x 280)
- Leaderboard (728 x 90)
- Half page (300 x 600)
- Large mobile banner (320 x 50 and 300 x 250)
What Is the Ideal Google Banner Ad Size?
There is no single Google Banner Ad size that guarantees success every time.
Although it’s highly recommended to spend time creating assets around the most common and top-performing ad sizes, your Display campaign success depends on many other factors. For example, some Google Banner Ads you have may perform better with a particular website publisher, and do poorly on others.
What’s critical is the correct audience targeting and user messaging and offer, depending on your audiences’ segmentation and position in the marketing funnel.
Then focus on the creatives used – images, animation, colors, fonts, etc. – and how they support your audience’s interests and your brand’s messaging and offer.You need to bring all these variables together to increase your probabilities of success.
However, you’re not done yet. Once your Google Banner Ads go live, and you start seeing impressions and clicks, you need to analyze which of your ads perform best.
Do A/B testing on your banner elements and identify which elements affect your banner ads’ clickability and engagement. Concentrate on fine-tuning the ad sizes that give you the best results.
Investigate further. Do some banner ad formats perform better on some publishers or target placements? Which creatives or copy have better CTR performance?
Invest more of your time and budget on those, and continue fine-tuning and testing them. Over time, you will find what works best for your business.
What Are Google Banner Ads Best For?
Google Banner Ads are best for prospecting, raising brand awareness, and remarketing.
You can use Google Banner Ads for awareness marketing using non-branded campaigns. You can also use Google Banner Ads for brand affinity marketing through branded campaigns.
When industry competitors congest the search engine results, use Google Banner Ads instead. Their main value is in the wider reach and affordability they offer.
Prospecting, brand awareness and remarketing campaigns using conventional Google Search ads can be very expensive. Google Banner Ads bypass a lot of the costly competition from other networks, while casting a wider net.
If your marketing goal is to build brand awareness in a more cost-effective way, use Google Banner Ads. There is less competition for inflated keyword bids, so you’re more likely to reach users actively searching for your products or services.
In the Google Display Network (GDN), the user intent is different from in the Google Search Network (GSN). The GDN users’ primary interest is the app or website content itself, so the Google Banner Ad has an indirect, secondary role. However, with tighter, more relevant targeting, remarketing can be limitless, although it involves audience development beyond the Google Ads platform.
On the other hand, even if audience intent is not as strong as in Google Search, you get a lower cost-per-click (CPC) with Google Banner Ads. You also get many more impressions for each Google Banner Ad, since your banner ad appears across GDN’s 35 million apps and websites.
Also, although the standard Click-Through-Rate (CTR) for Google Banner Ads is below 0.5%, it’s countered by the vastly increased volume of targeting prospects outside search engines and social networks. This increased variety of targeting options outside of keywords allows you to access the majority of internet users through website placements.
Your main focus in using Google Banner Ads should be to find the right audience size using strict targeting criteria. To estimate how much revenue you can earn from Google Banner Ads, you can use an ad revenue calculator.
Google Banner Ads Targeting Options
With Google Banner Ads, you have several options for customizing audience targeting.
The GDN allows you to define your audience in a ways search engines can’t. You can target for more than just keywords, so you’re not limited to the keywords that will rank you well in Google SERPs.
Aside from the usual targeting for demographics, you can target websites by audience affinities, in-market segments, and custom-intent keywords. You can even hand-pick website placements that match your target audience, or target for specific topics.
1. Audience affinities targeting
Affinity audiences are Google users with similar interests, such as beauty, cooking, electronic gadgets, fashion, home decors, music, sports, travel, and wellness.
These interests are expansive categories, so it’s important to narrow them down into further sub-categories with more specific targeting criteria. Otherwise, mainly relying on Google Ads’ default options can be very expensive.
For example, for the affinity category of “Sports & Fitness”, you can further narrow it down to “Sports Fans” and then “Water sports enthusiasts” if that’s what your business’ target customers are.
Use Google Analytics to pinpoint exactly which affinity audiences give the highest conversion rates on your app or website.
Google Ads also creates a “similar audience” or “similar segments” based on the audiences created in Google Analytics. These audiences are often more focused in size, which makes them ideal for testing.
Starting May 1, 2023, though, Google Ads will no longer generate similar audiences or similar segments. Instead, different campaign types will offer different solutions. This helps leverage businesses’ first party-data, reach the right audiences, and improve their campaign performance so they can optimize better for their business goals.
For Display campaigns, Google recommends turning on optimized targeting to reach additional relevant and expanded audiences and optimize for conversion goals.
2. In-market segment targeting
In-market segments are Google users interested in broad groups of products and services, such as personal finance including online savings accounts, home and garden, parenting, real estate, and travel.
Google defines these segments based on the users’ historical views, clicks, and conversions on previous content. Then, Google further groups them into sub-categories, which could easily translate into millions of users.
What makes in-market segments different from affinity audiences is that in-market segments are already on the verge of making a purchase. Affinity audiences may have the interest in a particular area, but may not yet intend to make a purchase. When starting for Google Banner Ads, it is best to start with in-market segment targeting.
To control audience size for in-market segments, compare them with your Google Analytics data, which align with those on Google Ads. Google Analytics should show you which in-market segments have the highest conversion rates.
Also, since Google Analytics has the tools for identifying and building data-driven audiences from which Google Ads can learn from and optimize, stop relying on educated guesses for targeting. It is better to optimize your use of Google Analytics as a partner of Google Ads.
3. Custom intent audiences targeting
In custom intent targeting, Google serves your ads to users on various websites that have some contextual connection to the website URL or address and keyword you provided to Google.
So, Google can show your banner ads to users who are “likely to be interested” in specific website URLs or keywords, including people who have recently searched for your submitted keywords.
What makes this different from the other targeting methods is that you are not targeting websites that use your specific keywords, and Google is not placing your banner ads exclusively on specified website URLs.
4. Specific website placement targeting
You provide Google with specific website placement URLs, and Google shows your banner ads on these specific websites. This option provides you with tighter, more controlled targeting because it limits display placements to the websites you have indicated.
On one hand, you can save money by being ultra-specific. On the other hand, you could also be missing out on more mainstream websites that your target audience more actively visit. These websites may or may not have content related to your suggested keyword or website URL.
With custom affinity (based on interests) and custom intent (based on keyword and website URL) targeting, Google can target these users at other online destinations. Google knows that these websites are also sites that users of your submitted keywords and website URLs also visit.
5. Topic targeting
With topic targeting, Google can show your banner ads only on webpages with your specified topic. These topics may align with interests or affinities, or they may fall outside these categories.
Topic targeting is an alternative to deeply researching and selecting website placements for a specific interest, without knowing the impact of those placements.
Fundamentally, with Google Banner Ads, you don’t need a huge budget. You just need to set the right targeting options for your marketing goals.
Why Are Google Banner Ads Important
Google Banner Ads are important for your business since they help you expand your reach beyond Google Search and social media.
Banner ads grab potential customers’ attention, help increase customer traffic, and sell your products or services. They are easy to create and easier to launch compared to most other forms of online advertising.
You can easily determine your banner ads’ effectiveness by checking on their CTRs. You can keep your costs down, too, since they don’t require a minimum budget. Google only recommends an average daily budget which is your estimated lowest budget amount at which you wouldn’t lose any impressions. You can also lower your bids in campaigns limited by budget or let Google Ads automatically bid for you.
Specifically, Google Banner Ads help you:
1. Reach people in multiple places
With GDN’s millions of apps and websites, you can extend your reach beyond Google Search. Even when people don’t know your business exists yet, Google Banner Ads help put you out there to the right audiences, all throughout the world.
2. Build campaigns around your goals
With Google Banner Ads, you can aim for building awareness and consideration for your brand, product, or service or for driving sales, leads, and website traffic.
Through optimized targeting and smart bidding, Display campaigns use machine learning solutions across targeting, bidding, and formats to reach existing and new audiences.
3. Optimize for conversions
Optimized targeting lets you find the best performing audience segments that include potential customers who are highly likely to help you with your conversion goals.
Smart bidding uses machine learning to optimize for conversions in general, or conversion value per auction in particular, saving you time and improving your ad performance.
How GDN and Google Banner Ads Work

The Google Display Network helps you find the right audience with its targeting options that strategically show your message to potential customers at the right place and the right time.
Here are some examples of how you can approach targeting with Google Banner Ads, using responsive display ads.
1. You can engage existing customers or find new customers using audience segments.
In-market and affinity segments, for example, help you find new prospective customers who are already interested in your products or services. You can also use your other data segments from other targeting options to re-engage people who previously clicked on your Google Banner Ads and visited your site.
2. You can also drive more conversion using automation.
Automated targeting can increase conversions by finding high-performance audience segments based on your existing landing page and audiences. Over time, by automatically optimizing these segments, Google Ads learns which audience segments work best for your business.
Automated bidding helps you adjust your bids to meet your return-on-investment (ROI) goals. Using smart display campaigns, the best of automated targeting, bidding, and creatives are combined and optimized to maximize your Google Banner Ads conversions.
Where do Google banner ads appear?
Google Banner Ads are placed in high-traffic locations in webpages where the eyes of users often wander. These locations are usually at the top of the page, at the bottom of the page, or inline with the app or website content as the user scrolls through their pages.
When do Google banner ads show?
Google Banner Ads changes can take 12–24 hours to apply and may not show right away. Keep this in mind while creating a new campaign or making changes to an existing campaign. You may want to set up your campaign a few days before the launch and set the start date in the future.
How do I create a Google banner ad?
Google Banner Ads are fairly easy to make. You can create them from Google Ads or from Google Web Designer.
From Google Ads
- Create a Google Ads account if you don’t have one yet.
- Log in to your Google Ads account and click on the Campaigns at the top of the screen.
- Click the Campaigns dropdown, click on Campaigns, then select New campaign.
- Select your goal (Brand awareness and reach, Website traffic, Leads, or Sales). If you don’t have a goal in mind yet, you can also select Create a campaign without a goal’s guidance.
- Select Display as the campaign type and Standard display campaign as the subtype.
- Provide the URL for your business’ website.
- Enter the name of the campaign and select Continue.
- Select your campaign settings in terms of the locations and languages where you want your banner ads to appear.
- Set your budget and bidding strategy.
- Choose your targeting strategy.
- Create responsive display ads.
- Upload your assets (images, headlines, descriptions, logo design, videos). Google will automatically generate ad combinations for apps, websites, Gmail, and YouTube. To improve ad effectiveness. Upload at least 5 images, 5 headlines, 5 descriptions, 2 logos, and a video.
- When done, click Add to ad group.
- On the Review page, address potential issues described in Google’s alert notifications by clicking Fix it in the notification.
- Once you’re ready to publish, click Publish campaign.
From Google Web Designer
Google Web Designer is an advanced web application that lets you design online ads and videos, develop code, add media and interactivity, create and maintain advanced workflows – all at no cost. You can download and use Google Web Designer here.
To create a new Google Banner Ad:
1. Select File > New from the top menu of your downloaded Google Web Designer.
2. In the Create New Blank File dialog, choose Banner as the ad type.
3. Provide the information asked for:
- Name of the banner ad
- Location – where you want to save the file
- Ad environment – where you want the banner ad to run (Display & Video 360, Google Ads, Google AdMob, or non-Google ad)
- Dimensions – either check Responsive layout or manually set the dimensions
- Animation mode – select the animation mode that you want to initially use (this can be changed later). Quick mode lets you animate your ad scene by scene, while Advanced mode lets you animate individual elements on their own timeline.
4. Click OK.
5. Design the banner ad by:
- Adding images, video, and other assets
- Arranging elements on the stage
- Optionally creating animations or adding components
- Adding breakpoints if you’re creating a responsive ad, then restyling each new size range.
6. Add a Call To Action (CTA).
7. Preview your banner ad in your browser to make sure it looks and behaves as expected. Use the Preview button instead of directly opening the source HTML file from your browser.
8. Click Publish and select where you want to publish to (local, Google Drive, Studio, Display & Video 360). You may then use the published files to traffic your ad on the ad network you choose.
Top 10 Best Practices For Google Banner Ads
We strongly recommend these top ten best practices for Google Display or Banner Ads, which we collected from different expert sources across the web:
1. Follow Google Ads policies.
Study Google Ads policies first before even creating your Google Banner Ads. These policies are for ensuring safe and positive experiences for all users.
Follow these policies when you do finally create your ads. Otherwise, your ads won’t even be published as they will be disapproved. Remarketing lists will be disabled.
If the violations are very serious, your account will be suspended.
Google conducts periodic compliance reviews and may contact you to request information related to compliance.
2. Separate your Google Display Network (GDN) campaigns from your Google Search Network (GSN) campaigns.
Keep your Search and Display Networks distinct and create different campaigns on them, simply because the user intent in each network is different.
This way, too, you will have better control over your campaign and ad performance, budgets, and targeting options. You will also have better success in optimizing the different campaigns to meet the needs of different users between the two networks.
Speaking of separating campaigns, also separate your new users from your remarketing audiences. Awareness campaigns work on different user intents and customer journey stages from remarketing campaigns.
3. Make ads look as your brand.

Create banner ads that are consistent with your brand image and messaging. This helps establish connections with your target audiences and paves the way for building long-term relationships over time.
Your banner ads must be a part of the bigger ecosystem of your business vision, mission, and strategy, as well as your marketing research, plan, and strategy.
4. Provide a relevant landing page.
When prompted to add your URL as you create your ad, make sure that the URL you provide leads to a relevant landing page.
Your efforts shouldn’t end with simply creating your banner ads. Think about the user experience if users click on your ads. What will they see? Is your landing page optimized for conversions? Does your landing page answer your users’ question or solve a pain point?
There should be a seamless transition from the user’s being attracted to your banner ad, clicking on it, and landing on the page that convinces them to convert.
5. Use responsive display ads.
Google automatically optimizes your responsive ads to yield the best possible results. One way it does this is by testing multiple campaigns against each other, so it knows which best fit your campaign goals and should be prioritized.
Use all 5 headline and description fields, all 15 image slots, and add your logo in different dimensions, so Google can come up with as many variations as possible.
With responsive ads, we also recommend creating multiple campaigns, segmenting them by unique selling propositions (USPs) and desired user actions.
6. Include your logo.
Users will not know who you are if you don’t include your logo, which is an important part of your brand identity. It should be prominent in your banner ad, and the first thing the user sees.
7. Your headline and description should be clear and compelling
Your headline and description copy, aside from your images, are what draw users to read and click on your ad. The way they’re crafted can spell the difference between users clicking on your banner ad or moving on to click on a competitor’s ad.
So, it’s important that your headline and description copy match your searchers’ intent, are aligned with your target keywords, and address the searchers’ pain point with a clear solution.
8. Optimize your images and avoid collages.

Follow Google Ads policies and guidelines for images, such as those on aspect ratios and the right file types and maximum sizes.
Obviously, don’t use blurry images. Avoid images with borders. Don’t use image filters. Do not overlay your logo, text, or buttons on images. Upload logos with transparent backgrounds so Google has maximum flexibility in automatically creating your banner ads. The white space or padding around your logo should be 1/16th of the logo size. Focus your images on your products and services.
Use a single image for every asset. Don’t upload an asset that contains a collage of multiple images in the same composition.
9. Monitor frequency.
To avoid ad blindness or banner blindness/noise, monitor how often users are seeing your ads as well as the number of unique users who saw your banner ads.
Banner blindness is when users consciously or unconsciously ignore banner-like information when they visit websites. Google advises blending, contrasting, and complementing ad colors to minimize this in the first place.
In Google Ads, add specific reach columns for your monitoring.
As your unique users and frequency numbers change, monitor how your CTR, conversions, conversion rates, and other key performance indicators (KPIs) change.
Then, use these data to update your frequency cap settings and limit your ad impressions in your Google Display Network (GDN) campaigns. Do this by day, week, or month. It’s a fine balance to maneuver monitoring how your targeting options are engaging with your ad creatives.
10. Review and exclude placements.
Regularly review your ad placement report and adjust your campaign and ad settings accordingly.
For example, if you don’t want your banner ads to appear on mobile apps at all, then exclude all mobile app categories from your campaigns. If you’re using targeting methods such as keywords or topics, Google puts them on automatic placements.
You can also opt for managed placements. This is a Google Ads feature that allows advertisers more control over where their ads appear. You can then select specific apps and websites where you would like your ads to appear. But then again, if you’re looking to expand your reach, using managed placements can adversely affect the extent of your reach.
FAQ
Does Google do banner ads?
Yes. Google Banner Ads are the most common type of display ads in the Google Display Network (GDN), so they are often also called Google Display Ads.
Are Google banner ads free?
It’s free to create a Google Ads account and Google banner ads. You only start paying when app users or website visitors take action on your banner ad, such as clicking your banner ad to visit your site or to call your business. The average cost per link on the Google Display Network (GDN) is less than $1.
How to add Google banner ads to app?
Essentially, add by using Google AdMob. It is easiest if you do it through Google Firebase, Google’s Mobile Backend-as-a-Service (MBaaS). Otherwise, you have to do it manually or hire a pre-vetted expert to do it for you.
Are Google Banner Ads Right For Your Business?
Google Banner Ads are all about who you’re showing them to and where. Instead of targeting only keywords, you also target audiences, placements, and topics.
If your business’ current priority goal is brand awareness, followed by remarketing, then Google Banner Ads can be right for you. Google Banner Ads can achieve high volumes of relevant impressions.
Google Banner Ads are especially helpful if you are in a niche market and your Search campaigns have been lethargic. A good banner ad can then trigger more branded searches that can boost your Search campaigns.
You can amass a very powerful reach on the Google Display Network (GDN) with the right attention to targeting. The network’s affordability, as well as the separation from the competition, makes it a viable marketing option.
Bottom line, while the Google Search Network (GSN) can reach people while they search for specific goods or services, the Google Display Network (GDN) can help you capture someone’s attention earlier in the buying cycle. You can put your ads in front of people before they start searching for what you offer, which can be key for your overall advertising strategy.
This guide has detailed for you all you need to know to start doing Google Banner Ads well, if you want to do them yourself or with your team.
Alternatively, if you don’t want to be bothered by the nitty-gritty of implementing Google Banner Ads, you can also hire a Google Ads Specialist who can do all the work for you. Schedule a free consultation call with one now.
Still, what you’ve learned from this guide can help you collaborate better with your Google Ads Specialist. So, either way you decide to proceed, it’s a win-win.