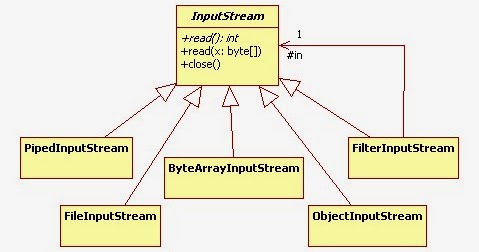
Difference between FileInputStream and FileReader in Java
Reader can either use default character encoding of platform on which your Java program is running or accept a Charset object or name of character encoding in String format e.g. “UTF-8”. Despite being one of the simplest concept, lots of Java developers make mistakes of not specifying character encoding, while reading text files or text data from socket.
Remember, if you don’t specify correct encoding, or your program is not using character encoding already present in protocol e.g. encoding specified in “Content-Type” for HTML files and encoding presents in header of XML files, you may not read all data correctly. Some characters which are not present in default encoding, may come up as ? or little square.
Once you know this fundamental difference between stream and reader, understanding difference between FileInputStream and FileReader is quite easy. Both allows you to read data from File, but FileInputStream is used to read binary data, while FileReader is used to read character data.
FileReader vs FileInputStream Java
Since FileReader extends InputStreamReader, it uses character encoding provided to this class, or else default character encoding of platform. Remember, InputStreamReader caches the character encoding and setting character encoding after creating object will not have any affect.
Let’s see an example of How to use FileInputStream and FileReader in Java. You can provide either a File object or a String, containing location of file to start reading character data from File.
import java.awt.Color; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; /** * Java Program to read data from file as stream of bytes and stream of * characters. * It also highlight key difference between FileInputStream and FileReader that * FileReader is meant for reading streams of characters. * For reading streams of raw bytes, consider using a FileInputStream. * * @author Javin Paul */ public class HowToReadFileInJava { public static void main(String args[]) { // Example 1 - Reading File's content using FileInputStream try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("data.txt")) { int data = fis.read(); while (data != -1) { System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(data)); data = fis.read(); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("Failed to read binary data from File"); e.printStackTrace(); } // Example 2 - Reading File data using FileReader in Java try (FileReader reader = new FileReader("data.txt")) { int character = reader.read(); while (character != -1) { System.out.print((char) character); character = reader.read(); } } catch (IOException io) { System.out.println("Failed to read character data from File"); io.printStackTrace(); } } } Output: 4157532d416d617a6f6e205765622053657276696365da4 74f4f472d476f6f676c65da4150504c2d4170706c65da47 532d476f6c646d616e205361636873 AWS-Amazon Web Service GOOG-Google APPL-Apple GS-Goldman Sachs
Our first example is reading data from file byte by byte, so its bound to be very slow. read() method from FileInputStream is a blocking method, which reads a byte of data or blocks if no input is yet available. It either returns next byte of data, or -1 if the end of the file is reached.
On the other hand, in example 2 are reading data character by character. read() method from InputStreamReader, which is inherited by FileReader reads a single character and returns the character read, or -1 if the end of the stream has been reached.
That’s all on difference between FileInputStream and FileReader in Java. Bottom line is use FileReader or BufferedReader to read stream of characters or text data from File and always specify character encoding. Use FileInputStream to read raw streams of bytes from file or socket in Java.