A Roadmap for Your Machine Learning Career
A Roadmap for Your Machine Learning Career
Image by Author | Created on Canva
Are you looking to make a career in machine learning? If so, this guide is for you.
Machine learning is an interesting field with a lot of potential to solve real-world problems. However, going from a novice to a professional requires a structured approach that not only focuses on technical skills but also on understanding real-world applications, software engineering practices, and industry expectations.
And this guide will walk you through every step of this journey, helping you build a solid foundation and set you up for success in your ML career.
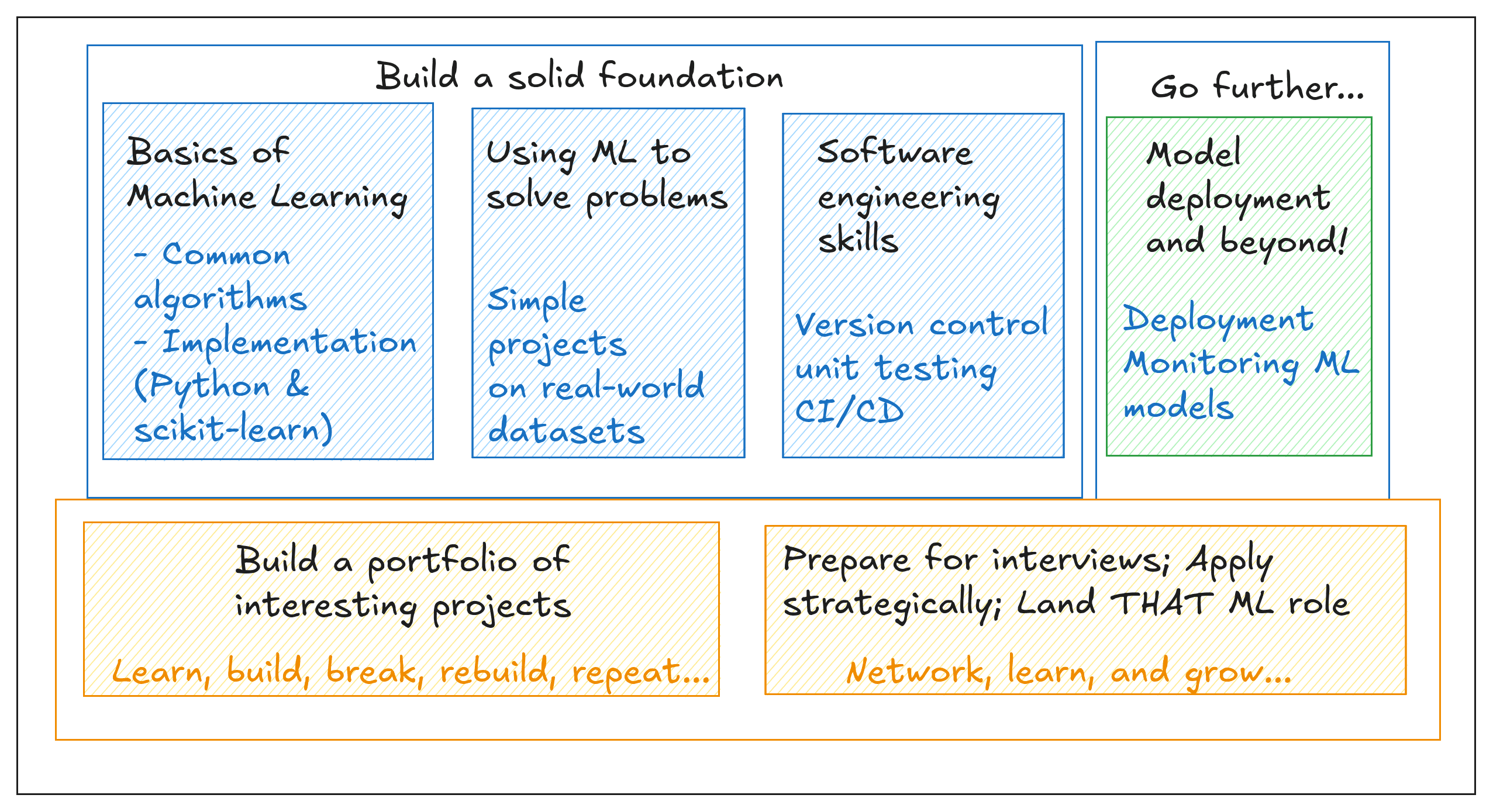

Machine learning roadmap
Image by Author
Start with the Basics of Machine Learning
To become proficient in machine learning, you need to start with the basics. You’ll first need to learn how common machine learning algorithms work and how to use ML frameworks and libraries to build models. These frameworks abstract the complex math behind algorithms and allow you to focus on building models.
You can start with scikit-learn as it’s super simple to work with. Once you’re comfortable, you can proceed to frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch. Besides the significance, learn to do the following with scikit-learn:
- Data preprocessing
- Model training and evaluation
- Hyperparameter tuning
- Cross-validation
Start small by practicing on standard datasets. Learn to clean and visualize data, train models, and evaluate performance.
Understand How to Solve Real-World Problems with Machine Learning
Once you’re comfortable with the frameworks, it’s time to apply machine learning to real-world problems. This step will not only help you solidify your knowledge but also demonstrate your ability to deliver solutions that can impact businesses or society.
Key steps in problem solving include:
- Problem definition: Understand the business problem before jumping into the data.
- Data collection and cleaning: Real-world data is messy. Knowing how to collect and clean data is essential.
- Feature engineering: The quality of features often defines the success of a model. Understand techniques like one-hot encoding, scaling, and creating domain-specific features.
- Model selection: Choosing the right algorithm for the task is critical. Learn which models are suitable for classification, regression, and clustering problems.
- Model evaluation: Go beyond accuracy—use metrics like ROC AUC, F1 score, and precision-recall—to properly evaluate your models.
For practice, try to work on real-world projects like:
- Predicting customer churn
- Building a recommendation system
- Creating a fraud detection model
Learn Software Engineering Skills
Machine learning engineers are, first and foremost, software engineers. Understanding the fundamentals of software engineering will make you more effective at scaling ML solutions in production.
Key software engineering concepts to learn:
- Version control: Use Git for managing code, and understand how to collaborate in a team.
- Clean code and best practices: Writing clean, modular, and reusable code is essential. Get familiar with SOLID principles and design patterns.
- Testing and debugging: Unit testing, using frameworks such as PyTest, is important for validating your ML code.
- CI/CD pipelines: Automate testing and deployment through Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment pipelines.
Focus on Model Deployment and Beyond
Understanding how to deploy models is a key skill for ML professionals. You can deploy your machine learning models to get real-time predictions in production environments.
Steps for model deployment:
- Use frameworks like Flask, FastAPI, or Django to create APIs that serve your models.
- Containerization is a key skill for ensuring that your models run consistently across different environments. You can learn Docker and Kubernetes to containerize applications.
- Learn how to deploy models on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. This involves using services like AWS SageMaker.
- Once in production, models need monitoring for performance degradation. Use tools like Prometheus and Grafana to build dashboards and alerts for model drift.
You should also be aware of post-deployment considerations such as:
- Retraining models based on new data
- Handling model updates and A/B testing
- Scaling models to handle large volumes of requests
Build a Portfolio of Interesting Projects
A strong portfolio showcases your skills and problem-solving ability to potential employers. Your goal is to demonstrate a variety of machine learning applications, from supervised learning to deep learning and unsupervised techniques.
Here are some tips to building a great portfolio:
- Choose diverse projects: Work on a variety of projects: simple regression models, classification tasks, natural language processing, computer vision, and more.
- Build end-to-end solutions: It’s important to showcase complete workflows, from data acquisition and preprocessing to deployment.
- Showcase on GitHub and similar platforms: Make your code accessible and well-documented. If possible, use Jupyter Notebooks to explain each step of the process.
- Contribute to open source projects: Contributing to ML frameworks or libraries helps build credibility and demonstrates your coding ability.
If you’re looking for ideas, check out:
Interview for Machine Learning Roles
Landing your first ML job requires preparation not only in terms of technical skills but also interview strategies.
Common interview phases include:
- Coding challenges: Expect coding problems focused on algorithms and data structures. You can practice on sites like Leetcode and HackerRank. is an excellent resource for practice.
- Technical interviews: Be prepared to explain ML concepts, algorithms (e.g., decision trees, SVMs), and evaluation metrics. You should also be able to explain your projects.
- Behavioral interviews: Employers will also evaluate your soft skills. Practice answers to questions about teamwork, problem-solving, and your motivation for ML.
- System design interviews: Sometimes, you may have to go through an ML system design interview. You might be asked to design an ML system at scale. Understand how to design pipelines for data ingestion, model training, and real-time prediction.
That sums up the typical interview process. Once you land the role, you can learn and grow as you work on more projects.
Wrapping Up and Next Steps
As you advance in your machine learning career, continuous learning and networking become necessary for staying ahead. Machine learning is quite a challenging field—with new techniques, tools, and research emerging regularly.
Learning continuously, engaging with the community, and building your professional network, you can have a successful machine learning career.



